Air Quality Machine Learning Classifier
This research project was part of the Machine Learning class at Ramapo College (CMPS-320).
It presents the classification of air quality levels in India based on data that has been collected prior to and during the Covid-19 pandemic. The data was collected in order to identify the effects of shutting down the world for several months on the quality of air and could later be used to define the necessary precautions that need to be taken in order to decrease humans’ negative effects on the quality of air and our environment as a whole.
The Dataset used in this research was extracted from Kaggle and is called “Air Quality: multiclass classification”. It consists of 16 columns and 26,219 entries. Each entry contains the date and city in which the data was measured, as well as different columns containing the levels of different pollutants such as PM2.5, PM10, O3, etc. in the air. The last column is called “Air_quality” and contains the quality of air in that specific entry based on the different pollutant levels. The “Air_quality” column is classified into 6 different categories- Severe, Very Poor, Poor, Moderate, Good, and Satisfactory.
The first step in this project was to generate and additional column- “Air_quality_numeric”, which will hold values from 0 to 5, each representing an air quality category. Later, different Machine Learning classification models were applied to the dataset.
The following models were experimented with in this research:
- Stochastic Gradient Descent
- Random Forests Classifier
- K-Nearest Neighbors
- Decision Trees
- Support Vector Machine
- Extra Trees
The Following are the results of applying the Extra Trees Classification model to the dataset:
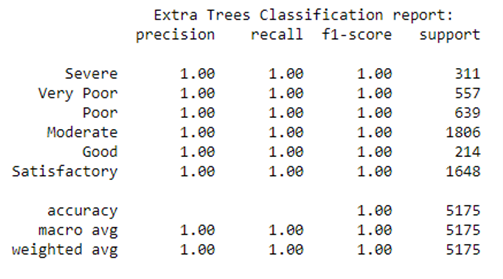
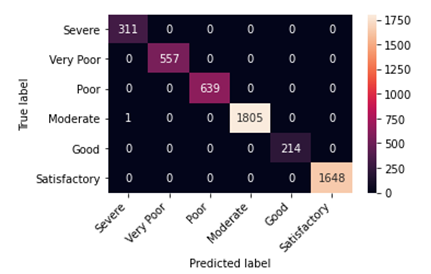
For the full Project you are welcome to visit my GitHub repository- Link to GitHub Repository